HVDC
In most parts of the world, it takes time, a lot of it, to get the necessary permits to build a new transmission line. While few dispute the benefits of and need for more electric transmission, many oppose the lines to be built. The reasons can be several, but in most cases, it comes down to NIMBY (Not-In-My-Backyard).

Pacific Intertie, a breakthrough transmission system at its time, initially, 1969, with a capacity of 2500 MW. With subsequent expansions the 400 kV HVDC line and the two 500 kW HVAC lines can bring 7900 MW of predominantly hydro power from the Pacific Northwest to the Los Angeles area. Photo by the author.
The common denominator for transmission projects moving ahead is thorough planning and persistence in working with public opinion and permitting authorities. For individual projects creativity and unconventional approaches can be effective enabling the project to happen. Below are some ongoing projects worth watching and learning from.
CONTINUE READING >>
On February 24 Russia started an unprovoked full-scale invasion of Ukraine. It has resulted in colossal damage and sufferings. How the war will end nobody knows, but it seems clear that Ukraine will remain a free, independent, and democratic nation, while Russia will achieve truly little, if anything of its goals.
The war in Ukraine will also have unintended and significant energy and environmental consequences in all Europe. For some countries there will be changes in the direction of their respective energy structures and plans. In other cases, the direction will remain unchanged, but the speed of change will accelerate.
CONTINUE READING >>
The infamous “battle of currents” 1888-89 between Thomas Edison on one side and Nicolaus Tesla and George Westinghouse on the other side, was about the future of the electric system. Which was the superior technology, Direct Current (DC) or Alternating Current (AC)? AC won, and for over half a century it looked like an outcome with the winner takes all.
CONTINUE READING >>
The Global Energy Interconnection Development and Cooperation Organization (GEIDCO) was formed in March 2016. The purpose is to promote the sustainable development of energy worldwide. The vision of the Global Energy Interconnection (GEI) is “a clean energy dominant electric centric modern energy system that is globally interconnected, jointly constructed and mutually beneficial to all. It is an important platform for large scale development, transmission, and consumption of clean energy resources worldwide. In essence, GEI is Smart Grid + UHV (Ultra High Voltage) Grid +Clean Energy.”
CONTINUE READING >>
There is a slogan for electric transmission that it is not about how much power you generate. It is about how much you deliver. There is a lot of truth to that. It was the innovations of electric transmission well over 100 years ago that enabled the modern electric system by bringing remote generation to the load.
Today a robust transmission grid is a prerequisite to economically and reliably balance generation and load. With more variable generation resources on the system, wind and solar, transmission is again the enabler. However, regardless how strong the rational for strengthening the transmission grid may be, the opposition against building new transmission can be equally strong or stronger. At few places it is more evident than in Germany.

CONTINUE READING >>
In 2014 there were 3634 outages in the US electric system according to the Eaton Blackout Tracker. It affected in total over 14 million people. On average close to 4000 people were affected per outage, which on average lasted 43 minutes. 30 % of the outages were caused by weather and trees. 28 % were caused by faulty equipment and/or human error.
Almost all outages were at the distribution system level, Outages at the transmission level are very rare, but when they happen the consequences are bigger, affect more people and take longer time to restore. The Northeast Blackout in August 2003 hit 55 million people in United States and Canada. One month later the Italy Blackout had also about 55 million people in Italy, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia and Croatia losing power. As recent as in March this year 90 % of Turkey with 70 million people lost their power. The largest blackout so far was in July 2012 affecting half of India and 620 million people. In fact the grid collapsed for a second time in two days.
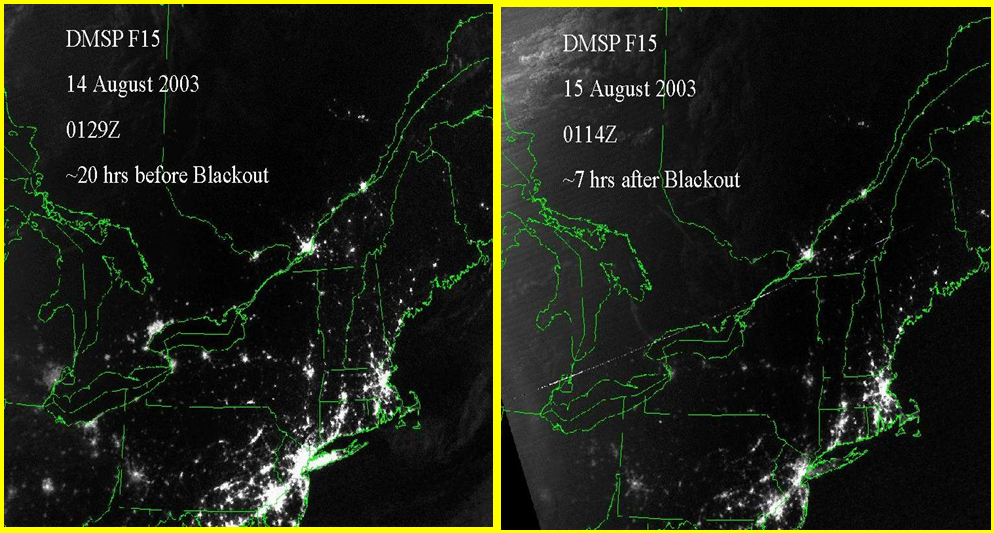
2003 Northeast Blackout. Satellite pictures before and after the blackout. National Geophysical Data Center (NOAA/DMSP).
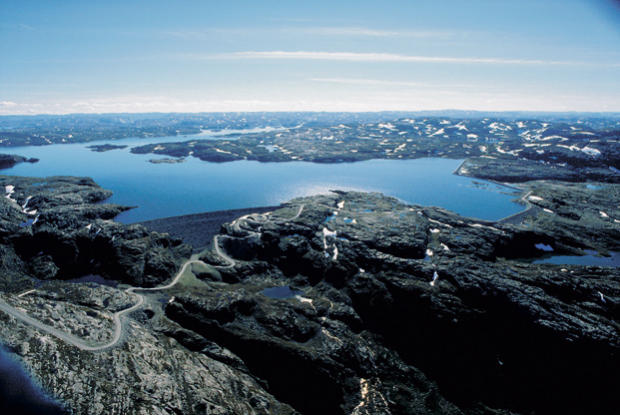
Lake Blåsjö, Norway.
Hydro storage is basically a renewable battery. Lake Blåsjö (“Blue Lake”) in Norway with a capacity of 7.8 terrawatthours (TWh) has become a symbol of Norway’s potential to become a “Blue Battery” for Northern Europe. To put the number in perspective 7.8 TWh would cover the electric consumption of over 750 000 residential homes. To accumulate the same amount of energy with lithium ion batteries it would take over 200 years of full production at Tesla’s planned Gigafactory.
Sunday August 18 Germany set a new renewable record. That day at 2 pm generation from renewable energy sources provided 75 % of all power needed to satisfy the total demand of electric energy.
Less noticed was that Burlington Electric Department, Vermont, in September with the purchase of a 7.4 MW hydroelectric facility achieved its goal of reaching 100 % from renewable energy.
While Germany’s August 18 record was a peak, Burlington’s 100 % is basically on a continuous basis.
What makes Burlington Electric’s achievement additionally impressive is that retail electricity rates in Burlington are less than half of the rates in Germany, 13.7 cents/kWh (time of use rate 2014) versus 36.25 cents/kWh (average 2013).
